| Overview of the SKF Seize-Resistant Ball Bearings |
|
The case for seize-resistant bearings

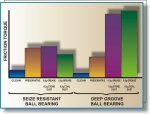
Investigations in the late 1960s into the standard deep groove ball bearing used in idler rollers revealed a tendency for them to become clogged with debris to the point where they could no longer rotate; High friction could also develop, causing over-heating and the possible risk of fire.
Taper roller bearings, whilst having higher load carrying capacities than deep groove ball bearings, are affected by misalignment. SKF research has shown, in idler rollers, that a combination of misalignment and abrasive contaminants causes severe wear to taper roller bearing cages.
Maintenance efficiency is essential for the smooth operation of conveyor installations. Relubrication is costly and difficult to control, both for grease quantity and ensuring all rollers are equally lubricated.
Seize-resistant ball bearings can operate for long periods without relubrication and are used in sealed-for-life idler rollers.
As manufacturers of all the main bearing types, SKF are able to take an objective view of fitness for purpose.
Since their development, well over 50 million SKF seize-resistant ball bearings have been keeping conveyors rolling on every Continent, effortlessly.
The fight against contaminants
Heavy duty conveyors biggest enemy is abrasion caused by the ingress of contaminants on protective seals and rolling bearings.
Even the most sophisticated and expensive sealing configurations have consistently failed in hostile environments, such as mines and quarries, resulting in bearing seizure.
Seizure causes:
-
High replacement and maintenance costs
-
Damage to high cost belting
-
Lost production due to downtime
-
Fire risk owing to friction
-
Unnecessarily high energy consumption
Investigations into idler roller seizures prompted SKF, in conjunction with British Coal (formerly NCB) and independent conveyor-roller manufacturers, to develop a purpose-designed ball bearing to solve the seizure problem head on.
The seize-resistant concept
SKF reluctantly accepted the inevitable penetration of grit, dirt and other abrasive contaminants into the raceways and rolling elements and designed seize-resistant ball bearings.
Its special internal design enables larger size balls to simply roll over the contaminants, crushing, milling and ejecting them in the process.
So, even when operating at moderate speeds, the bearings will continue to function.

Design characteristics
The largest possible ball size is used, while still adhering to internationally established inner ring bore and outside diameters.
Bearing capacity is increased, and more importantly, actual life expectancy extended.
A flexible one-piece nylon cage with its prong extension wiper between each pocket allows the use of larger balls, which increases the load carrying capacity. The wiper prevents the build-up of contaminants around the ball set.

To ensure ball rotation, even under contaminated conditions, special attention has been given to raceway design. This reduces skidding, a contributory cause of severe raceway damage and premature failure.
To avoid ring distortion and maintain a good interference fit in the roller housing, the outer ring has a larger than normal section height.
Land width either side of the raceways is reduced so as to discourage build-up of the abrasive materials.
Corner chamfers have also been reduced on both inner and outer rings, allowing smaller abutment heights.

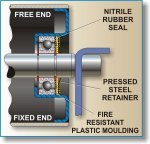
Design advantages
SKF seize-resistant ball bearings have the ability to operate in hostile environments. Whilst the raceway design is a major factor, the bearings other features now make it possible to considerably improve conveyor-roller design.
-
Expensive, elaborate labyrinth or complex rubbing seals are no longer essential.
-
The narrow width of the seize resistant ball bearing reduces end cap draw
-
Reduced distance between the idler roller end support and bearing centre minimises spindle deflection.
-
Special bore tolerances permit easy mounting.
-
Small corner chamfers mean reduced abutment heights.
-
Friction torque in contaminated rollers is reduced.
-
The SKF seize-resistant concept allows the manufacturer to reduce the costs of component parts and assembly whilst improving service life.