|
Mechanics of Disc Brakes |
|
Information courtesy of
![]()
1. Clamping force
The brake calipers of Svendborg Brakes are symmetrical. Available as dual spring or as monospring models. The thrust springs contained in the calipers force the brake pads against the disc. The clamping force is applied at right angles to the disc.
2. Friction force, braking force
The clamping force produces a friction force at the area of contact between friction pads and brake disc. The friction force is proportional to the clamping force applied, and depends on the friction coefficient of the pad material. The friction force counter acts the movement between pad and disc, actually occurring or in process of developing.
The sum of the friction forces produced by both caliper pads is called braking force.
3. Braking torque
The product of the braking force and its effective radius, as measured from the centre of the pads to the centre of the disc, is the braking torque.
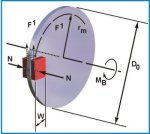
N = Clamping Force
= coefficient of friction
F1 = friction force
Fb = braking force
rm = radial arm of braking force
MB = braking torque
Do = brake disc diameter
W = pad radial width
The following relations exist:
friction force F1 = * N
braking force Fb = 2 * F1 = 2 * * N
braking torque MB = Fb * rm = 2 * * N * rm
torque radius rm = (Do - W) / 2