| Moment of Inertia |
|
Information courtesy of
![]()
For linear acceleration: F = m x a is valid when F is applied to a body m, to give an acceleration = a.
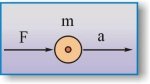
If we take the same body m and let it rotate around a fixed point P on a radius r.
The torque around P will be M = F * r
The linear acceleration a can be expressed as r * α = a where α is the angular acceleration.
Corresponding formula for rotation to linear motion, F = m * a(N) is M = J * α(Nm).
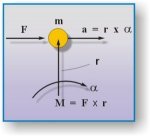
Multiply both sides of eqv F = m * a and exchange "a" with r * F * r = m * r * r * α ; M = mr2 * α
compared to M = J * α , J correspond to mr2.
The definition for moment of inertia J is:

GD2 / 4 = J kgm2
Don't use GD2 when calculating.
