Steel Protection
By Hot Dip Galvanizing & Duplex Systems
Information courtesy of: HOT DIP GALVANIZERS ASSOCIATION SOUTHERN AFRICA
Hot Dip Galvanizing of Sheet Metal
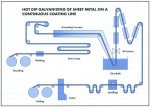
Hot dip galvanized sheet is produced on continuous zinc coating lines, (figure 16), from either cold rolled (thickness range 0.35 to < 1.6mm) or hot rolled (thickness range 1.6 to 3.0mm) steel coil to the requirements of SABS 934, ASTM A653, SABS ISO 4998 or SABS ISO 3575. Specification SABS 934 should no longer be referred to as it has been replaced by SABS ISO 4998 and SABS ISO 3575.
The coils are welded end on end to form a continuous strip. After degreasing the strip is pickled or oxidized. Oxides are then removed from the surfaces by reduction at 950C. At the same time the strip is soft-annealed. The surfaces of the strip, now chemically clean, are moved through a protective gas atmosphere and directly down into the zinc bath.The strip is withdrawn from the bath vertically and passed through air knives. Controlled jets of air or steam are blown through the knives, wiping the zinc coating to the desired thickness.
The galvanizing process yields an even zinc coated sheet with a bright smooth metallic finish, The zinc coating can be supplied with a regular or flattened minimised spangle finish. (Refer to 7.8 The Iron/Zinc Reaction in Continuous Galvanizing).
After cooling, straightening and treatment against wet storage stain, the strip is cut into suitably sized sheets or rolled into coils for delivery or subsequent painting and/or profiling (figure 16).
5.1 ZINC COATING SURFACE FINISH
The following surface finishes may be ordered to suit specific end-use requirements:
Regular Spangle (also known as normal spangle).
This is the unaltered, large, multifaceted crystal structure that occurs during normal solidification of a hot dip zinc coating on a steel sheet.
Variations in the size and brightness of the spangles are possible, depending on the galvanizing process and conditions, but this has no effect on the quality and corrosion resistance of the coating. Regular spangle is supplied for a wide range of applications where over painting for maintenance purposes can be undertaken at a later stage.
Figure 16. Schematic diagram showing the continuous hot dip galvanizing process for the coating of sheet.
Flattened Minimised Spangle
This is a zinc coating that is obtained by restricting the normal zinc crystal growth followed by the application of a skin pass process. The zinc coating thus obtained has improved formability and the zinc surface serves as an excellent base for pre-painting. post-painting and powder coating applications.
This finish is recommended for applications where a high gloss paint finish is required. It is available for zinc coatings of mass up to Z275. and a maximum steel thickness of 1.20mm if passivation is required, or a maximum steel thickness of 1.60mm if passivation is not required.
Zinc coatings of different thicknesses in accordance with SABS ISO 4998 or SABS ISO 3575 may be ordered to suit specific end use requirements. Certain coating grades are more readily available (tables 6 and 7 respectively).
The thickness and type of steel substrate is selected on the grounds of mechanical and structural consideration, whereas the thickness of the zinc coating is selected according to the corrosion-resistant life expectancy required.
Corrosion Resistance
The protection afforded by a hot dip galvanized coating under normal conditions of exposure is directly related to its thickness, The coating on sheet, normally stocked by retailers, is Z 275, which is suitable for a mild environment.
It is recommended that galvanized sheeting be overpainted timeously, preferably before the first appearance of red corrosion products. Where conditions require greater corrosion protection, a thicker class of coating i.e. Z 600 or the addition of a paint coating should be considered. In the case of the heavier coating. the sheet is not suitable for severe forming other than normal corrugating or curving.
Bend tests to evaluate the adhesion of the zinc coating are carried out and evaluated in accordance with relevant specifications (table 8). In addition to this, impact adherence cupping tests are performed on all products, irrespective of specification, to ensure good adhesion of the zinc coating.
Wet Storage Stain (White Rust)
When galvanized sheet in coil or sheet packs is stored under wet conditions, the galvanizing may be damaged by wet storage staining.
Rainwater or water vapour can easily be drawn in between tightly profiled or flat sheets, or between laps of coils by capillary action, Due to the absence of freely circulating air, this moisture cannot evaporate, causing unfavourable conditions that may result in white rust on galvanized sheeting.
Normally, light white staining on galvanized sheet is not serious, The wet storage corrosion process will stop when the affected areas are dried and exposed to the atmosphere. The discoloration will disappear within a few months during the normal weathering of the material. Where affected surfaces will form part of unexposed overlaps or other concealed areas that may be subject to extended periods of dampness, such areas should be cleaned and additionally protected.
Galvanized material must under no circumstances be stacked directly on a floor, See figures 19, 20 and 21. table 5 and Chapter 12 and also Removal of Wet Storage Stain, page 17.
5.2 SURFACE TREATMENT
The following surface treatments are normally used to reduce the possibility of wet storage stain during transport and storage:
Passivation
Passivation by potassium dichromate is normally applied to all galvanized material. In cases where this treatment may interfere with subsequent processing, the galvanized steel may be ordered without passivation, in which case oiling of the zinc surface is recommended.
Oiling
A special corrosion-preventive oil is used to coat galvanized sheet as an additional protection against wet storage staining during handling and storage. Oil is only used if requested.
If unoiled unpassivated galvanized steel sheet is ordered, proper protective packing should be requested to protect the material against the ingress of moisture during transport and storage. (Refer to Safe Storage, page 17).
5.3 CUT EDGE CORROSION RESISTANCE
The introduction of continuously galvanized coil that is subsequently cut into sheet lengths, has tended to focus attention on the behaviour of cut edges which are exposed to atmospheric corrosion. Sheet, thinner than 1.6mm is usually adequately protected at cut edges by the catholic action of the zinc coating Similarly, side trimmed edges seldom present a corrosion problem.
Thicker coatings provide superior cathodic protection.
| Zinc Coating Mass In Accordance With SABS ISO 4998 And 3575 | ||||
| Coating Designation |
Mass of
Coating* (both sides inclusive) g/m2, min |
Equivalent
thickness per side** m, min |
||
| Average | Individual | Average | Individual | |
| Z 100 | 100 | 85 | 7 | 6 (4,8) |
| Z 180 | 180 | 150 | 13 | 11 (8,5) |
| Z 200 | 200 | 170 | 14 | 12 (9,7) |
| Z 275 | 275 | 235 | 20 | 17 (13,4) |
| Z 350 | 350 | 300 | 25 | 21 (17,1) |
| Z 450 | 450 | 385 | 32 | 28 (22) |
| Z 600 | 600 | 510 | 43 | 36 (29) |
| Z 700 | 700 | 595 | 50 | 43 (34) |
Table 6. Mass per unit area of zinc coating
| Coating Designation |
Mass of Coating* (both sides inclusive) g/m2, min |
Equivalent thickness per side** m, min |
||
| Average | Individual | Average | Individual | |
| Z 1601,2† | 160 | 135 | 11 | 9 (7,7) |
| Z 275 | 275 | 235 | 20 | 17 (13,4) |
| Z 6003,4 | 600 | 510 | 43 | 36 (29) |
Table 7. Readily available zinc coating grades in Southern Africa
NOTES
| * | Not less thon 40% of the individual value should normally be found on each surface, indicated in brackets. | |||
| † | Although coating Classes Z 100, Z 160, Z 180 and Z200 are included in this table, these classes are not recommended for bare external applications but have been included far products which would subsequently be further protected by suitable paint systems. | |||
| ** |
For information only. The equivalent thickness is calculated from the following formula:
(7 is the approximate specific gravity of zinc) |
The letter Z in the coating designation indicates a pure zinc coating and the number denotes the total moss of the coating on both faces of the sheet (g/m2)
- Only available on 0.35mm full-hard material
- lscor specification only
- Not recommended for forming grades
- Not available on fall hard material
| Coating Designation |
Commercial Steel (CS), Forming Steel (FS) and Deep Drawing Steel (DDS) ASTM A653M-97 |
Structural Steel (SS) ASTM A653M-97# |
||||
| Galvanized Sheet Thickness t (mm) | Grade 230 | Grade 255 | Grade 275 | |||
| 0.4 ≤ t ≤1.0 | 1.0 < t ≤ 2.0 | t > 2 | ||||
| Z 275 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 |
| Z 600 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2.5 |
# Note: Grades 340 and 550 do not have specified requirements for this property.
Table 8. Ratio of the inside bend diameter to the thickness of the specimen
5.4 STRAIN AGEING
Galvanized steel sheet tends to strain age and this may lead to the following:
Surface markings from stretcher strain (Lder's lines) or fluting when the sheet is formed.
Deterioration in ductility.
It is recommended that the period between Anal processing at the mill and fabrication be kept as short as possible, preferably not exceeding six weeks.
5.5 PAINTING
Chemical conversion coatings and primers have been developed to provide good adhesion of subsequent paint films on zinc coated surfaces. To obtain optimum results it is essential to adhere to the instructions of the paint manufacturers, (Refer to table 9).
5.6 PRIMER COATED GALVANIZED STEEL SHEET PRODUCED IN A CONTINUOUS COATING LINE (CHROMAPREP)
Coating Process
CHROMAPREP is a registered trade name for cold rolled or hot dip galvanized steel sheet, coated with a high quality, flexible and corrosion inhibiting epoxy primer. The substrate is chemically cleaned and treated to ensure good adhesion of the chromate-rich epoxy based primer.
The coating has a nominal thickness of 4-6 micrometres applied by a sophisticated continuous roller coating process, permitting control of coating uniformity and film thickness within narrow limits, The primer coat is finally oven cured and is suitable for overcoating with most locally available finishing paint systems. (Refer to table 10).
CHROMAPREP is supplied with an epoxy primer coating on both sides of the steel sheet, CHROMAPREP with a cold rolled steel substrate may be used for indoor applications while CHROMAPREP with a hot dip galvanized substrate is usually intended for exterior use, after application of the desired final coating system.
| SITE
PAINTED GALVANIZED STEEL (The following matrix is a guideline only - refer to paint manufacturer prior to commencement of project |
||||||||||
| MATT FINISH | GLOSS FINISH | |||||||||
| Surface Preparation |
Patch Primer |
Primer | Intermediate Coat |
Finishing Coat |
Surface Preparation |
Patch Primer |
Primer | Intermediate Coat |
Finishing Coat |
|
| MARINE | ||||||||||
| New Galv. | GIC | - | - | A | A | GIC | - | H | J | J |
| Weathered Galv. | GIC | - | - | A | A | GIC | - | H | J | J |
| Partially Red Rusted | GIC + St3 | B | - | A | A | GIC + St3 | B | H | J | J |
| Previously Painted | C + abrade | - | - | - | A | C + abrade | - | - | - | J |
| INDUSTRIAL | ||||||||||
| New Galv. | GIC | - | - | A | D | GIC | - | H | J | J |
| Weathered Galv. | GIC | - | - | A | D | GIC | - | H | J | J |
| Partially Red Rusted | GIC + St3 | E | - | A | D | GIC + St3 | E | H | J | J |
| Previously Painted | C + abrade | - | - | - | D | C + abrade | - | - | - | J |
| RURAL | ||||||||||
| New Galv. | GIC | - | - | F | F | GIC | - | - | F | F |
| Weathered Galv. | GIC | - | - | F | F | GIC | - | - | F | F |
| Partially Red Rusted | GIC + St3 | G | - | F | F | GIC + St3 | G | - | F | F |
| Previously Painted | C + abrade | - | - | - | A | C + abrade | - | - | - | J |
Table 9. Site painted galvanized steel refer to Chapter 17).
Typical Primer Coat Properties
| Dry film thickness | 4-6 micrometers |
| Heat resistance | Max 120°C |
| Resistance to common water based detergents | Excellent |
| Resistance to mild solventst(1) | Fair |
| Flexibility(2) | 1T |
| UV - resistance(3) | Fair |
|
(1) Sensitive to common lacquer thinners, i.e. chlorinated or aromatic hydro-carbons and ketones but resistant to mineral turpentine, solvent naphta, mentholated spirits and paraffins. (2) No coating failure or loss of adhesion when bent around a mandrel mob a diameter as indicated (T is the thickness of the sheet in mm) (3) As is the cost with most epoxy primer coatings, CHROMAPREP is sensitive to ultra-violet radiation and should not be exposed to direct sunlight for prolonged periods before application of the final coating system. When directly exposed to sun-light (ultra-violet radiation) the final coat must be applied within seven days of being exposed. |
|
Table 10.
Corrosion Resistance
CHROMAPREP serves as a good corrosion inhibiting primer coat for subsequent painting. Resistance to corrosion creep is improved by using a galvanized steel substrate, which is strongly recommended for exterior applications.
Cleaning of Primer Coat Before Final Painting
Surfaces should be cleaned by removing surface contaminants by wiping with natural mineral turpentine, solvent naphta or methylated spirits, followed by a warm water detergent wash and a clean water rinse. Users are advised to ensure that thinners or adhesives used, are compatible with CHROMAPREP. The CHROMAPREP primer coat is slightly undercured to ensure good bonding of subsequent top coats. The liberal use of strong solvents can and will detach the primer coat, which may lead to premature peeling of the paint.
Common lacquer thinners such as chlorinated hydrocarbons or ketones (MEK) should not be used for cleaning purposes as these may affect the adhesion of the epoxy primer-coat.
Application of Paint Coatings
The required paint finish can be applied by normal spray, airless spray or brushing techniques. Usually an additional primer coat will not be necessary, but for most paints a better bond between the CHROMAPREP surface and the top coat, as well as a higher quality paint surface, may be obtained by application of a primer or intermediate coat for the selected paint systems.
Amongst current industrial products, the following paint systems can be applied to CHROMAPREP: alkyds, vinyls, acrylics, polyesters, powder-coatings. stoving enamels, epoxies and poly-urethanes.
5.7 PAINTED COLD ROLLED GALVANIZED STEEL SHEET PRODUCED IN A CONTINUOUS COATING LINE (CHROMADEK OR CHROMADEK PLUS)
CHROMADEK is the trade name for this pre-painted galvanized steel sheet. CHROMADEK is a colour coat comprising a Z 275 hot dip galvanized substrate, pre-primed on both surfaces with a 4 to 6 micron DFT primer.
CHROMADEK paint is then applied to both surfaces, a 20 micron DFT to one surface and about 8 micron DEW to the opposite surface (figure 17).
The colour coated products are coated on a sophisticated continuous roller coating line. The modern coating process permits good control of the important painting parameters and rigid quality control on each finished coil ensures that every batch conforms to specification. Excellent paint adhesion is achieved and corrosion resistance enhanced by careful preparation of the steel sheet under factory conditions prior to paint application. The paint systems are oven cured, The aesthetic appearance and durability of CHROMADEK cannot easily be achieved by conventional hand painted systems.
The coating is highly formable and provides additional protection under conditions where the corrosion resistance of unpainted galvanized sheeting may prove inadequate.
Corrosion Resistance
CHROMADEK is intended for exposure to rural, mildly chemically polluted or moderate marine conditions. Best results can be obtained through the correct application, good workmanship and maintenance procedures.
NOTE: CHROMADEK is not recommended for application in marine environments (area approximately 1km from the sea) or exposure to industrial environments where there is an accumulation of strong acid vapours. CHROMADEK PLUS is recommended for these conditions.
CHROMADEK PLUS is a colour coat comprising a Z 275 hot dip galvanized steel substrate, pre-primed on one or both surfaces with 20 - 25 micron DFT chrome free universal primer. Alternatively, only one surface is coated in accordance with the above and the other surface as per the standard CHROMADEK (4 - 6 micron DFT) CHROMADEK paint is then applied to both surfaces, both to 20 micron DFT (figure 17).
The Plus system has excellent physical properties, excellent flexibility, excellent corrosion resistance with excellent resistance to ultraviolet radiation (UV performance).
Corrosion Resistance
CHROMADEK PLUS is recommended for exterior building profiles in applications requiring high formability, good gloss retention, high colour stability and excellent corrosion resistance. It is suitable for corrosive environments such as industrial and marine environments. Marine environments can generally be defined as areas within 1 km of the sea (table 11).
5.8 FASTENING METHODS
Mechanical fastening systems such as rivets, self-tapping screws, bolts and nuts, spring clips and wire staples can be used, as well as various seaming methods including lock- and box seaming.
Where protection is needed, fasteners should, where possible, be:
hot dip galvanized; or
manufactured from a corrosion resistant material; or
electroplated and overcoated with a suitable top coat.
| PROPERTY | TEST CONDITIONS | METHOD | SPECIFICATION | TYPICAL |
| Resistance to colour change | QUV (1000 hours) | ASTM G53 | ΔE<5, e.g. Gemsbok Sand | |
| Resistance to chalking | QUV (1000 hours) | ASTM G53 ASTM D659 |
Rating Range: 1-2 |
|
| Resistance to
corrosion: - Edge creep - Blister size |
Salt spray (1000 hours) After 1000 hours After 1000 hours |
ASTM B117 ASTM A654 ASTM D714 |
≤ 3mm ≤ 8F |
< 2mm < 8F |
|
Flexibility: bend test |
ASTM D4145 |
3T. No adhesion loss |
2T. No adhesion loss |
|
|
Flexibility: reverse impact |
ASTM D2794 |
No cracks No adhesion loss |
No cracks No adhesion loss |
|
| Film hardness | ASTM D3363 | F - H | F - H | |
| Dry film thickness | NCCA 4.2.2 |
22m minimum inclusive of primer | 22m minimum inclusive of primer | |
| Gloss at 60 | At time of coating | ASTM D523 | 25 - 35% | 25 - 35% |
Table 11. CHROMADEK paint system properties.
Figure 17.
Cutting, Touch-up and Maintenance
Abrasive cutting or trimming of CHROMADEK sheeting on roof tops should be avoided. Should cutting be necessary, remove all Iron particles by vigorous brushing with a broom or bristle brush after cutting to avoid tarnishing the CHROMADEK paint surface.
In order to site cut a sheet with clean edges and no paint damage, a sheet nibbler is recommended.
Specially formulated air-drying touch-up paints are available. Care should be exercised to minimise overpainting as this might accentuate the defect, The ultra-violet resistance of air-drying touch-up paints is generally less than the oven-cured CHROMADEK finishes. Accordingly, touching-up of scratches should be done with a thin paint brush to minimise unnecessary overpainting. If aesthetically acceptable, it is recommended that minor scratches resulting from erection and rough handling be left uncoated as the galvanized substrate will offer adequate sacrificial protection against corrosion.
The life of a CHROMADEK painted surface can be extended and the appearance maintained by washing down periodically with water and a mild detergent to prevent any build-up of corrosive deposits, especially in marine or industrially polluted environments.The extent of the damage to CHROMADEK paint coatings is rather difficult to assess. In cases where the original gloss and colour have been retained, there should be no cause for concern. On proper drying of the moisture contained between closely nestled sheets, no further deterioration will occur, Where discolouration and/or signs of white corrosion products (except cut edges) are evident, such sheets should be substituted with new material.
Certain situations can create unusually aggressive conditions for the exposed, reverse sides of roof sheets. These include coastal locations (and therefore the risk of saline spray and deposits collecting on the exposed reverse sides of overhangs), extremely polluted industrial environments, and very low pitched roofs. In these or similar conditions, extra protection may be necessary. This can be achieved by specifying CHROMADEK PLUS to both surfaces.
Compatibility
Most materials used in contact with traditional galvanized steel can be safely used with CHROMADEK. Run-off water from Cor-Ten, lead or copper products, however, may cause staining and should not be allowed to come into contact with the painted surface.
Edge Protection
Generally cut edges on CHROMADEK sheets do not present a corrosion problem even in coastal areas as the galvanized coating will sacrificially protect the exposed steel. Small traces of white deposits on cut edges should therefore, not be a reason for concern.
5.9 THE HANDLING AND PROTECTION OF GALVANIZED AND PREPAINTED STEEL SHEET DURING STORAGE
Galvanized and prepainted galvanized sheet is known to perform exceptionally well when exposed to the elements. Under normal wet-and-dry conditions, e.g. when galvanized sheet is used as roofing and for cladding of buildings, a protective zinc oxide/zinc carbonate layer naturally forms on the exposed surfaces of the material, which improves the resistance against corrosion. In the case of pre-painted sheeting, the protective paint coating offers an additional physical barrier against the elements.However, the protective nature of these coatings may be seriously impaired when exposed to wet conditions for extended periods in the absence of air. The material is at its most vulnerable during prolonged storage without the necessary precautions.
Rain water or water vapour can easily be drawn in between tightly nested profiled or flat sheets, or between laps of coils, by capillary action (figure 19).
Due to the absence of freely circulating air, this moisture cannot evaporate, causing unfavourable conditions which may result in wet storage stain, often referred to as white rust" on galvanized sheeting. See Evaluation of Wet Storage Stain - table 5. In the case of prepainted sheeting these conditions may cause discolouration of the paint film and in extreme cases wet storage staining, similar to galvanized sheeting.
|
Figure 18. S-Rib galvanized steel sheeting - Z600 coating classification used for architectural applications. |
Figure 19. |
Wet storage stain may start soon after nested packs or coils of sheet are exposed to wet conditions and may affect the expected maintenance-free life of the sheeting unless arrested at an early stage. The material has to be thoroughly dried and exposed to freely circulating air to stop this corrosion process (figure 20).
Steps Taken to Protect Galvanized Sheet against Damage by Wet Storage Stain
It is standard practice to passivate the surfaces of galvanized sheet by chemical treatment during processing, in order to inhibit the occurrence of wet storage stain. Furthermore, galvanized sheet can be ordered with a special protective oil, which is supplementary to the normal passivation and is intended to provide additional protection during handling and storage.
In spite of these precautions, galvanized sheet cannot be entirely safeguarded against wet storage stain, especially when stored incorrectly under adverse conditions.
A special type of packaging is provided for flat sheets and coils. Users, who do not have the necessary facilities to temporarily prevent the ingress of moisture are advised to specify such protective packaging.
Every endeavour is taken by manufacturers to ensure that coated sheet products leave the works dry and in prime condition. Such products, whether despatched in coils or cut lengths, are packed, handled and loaded, under cover, onto vehicles where they are covered with tarpaulins or canopies.
Safe Storage
To prevent unnecessary damage to galvanized or colour-coated sheets, proper measures should be taken to prevent contamination by moisture while the material is still bundled or nested in stacks (figure 20).
Figure 20.
If not required for immediate use, coils or packs of sheets must be stacked on site under properly designed cover, clear off the ground and protected from wind-driven rain (figure 21).
Plastic tarpaulins which completely envelop packs of sheets or coils should not be used, as a sudden drop in ambient temperature may cause condensation of water vapour, which can easily be drawn in between nested sheeting by capillary action.
Ideally, deliveries of galvanized and colour-coated steel sheet to the building site should be scheduled for a storage period of not longer than two weeks prior to installation. Inspect the storage site regularly to ensure that moisture does not penetrate the stock.
Removal of Wet Storage Stain
Wet storage stain should rather be prevented than cured.
Although in extreme cases the protective value of the coating may be impaired, wet storage stain attack is often superficial despite the relative bulkiness of the corrosion product. Where surface staining is light and smooth without growth of the zinc oxide layer as fudged by lightly rubbing fingertips across the surface, the staining will gradually disappear and blend in with the surrounding zinc surface as a result of normal weathering in service.
When the affected area will not be fully exposed in service or when it will be subjected to a humid environment, wet storage staining must be removed, even if it is superficial. This is essential for the basic zinc carbonate film to form. The formation of this zinc carbonate film is necessary to ensure long term service life.
Light deposits can be removed by cleaning with a stiff bristle (not wire) brush. Heavier deposits can be removed by brushing with a 5% solution of sodium or potassium dichromate with the addition of 0. 1 % by volume of concentrated sulphuric acid. Alternatively, a 10% solution of acetic acid can be used. These solutions are applied with a stiff brush and left for about 30 seconds before thoroughly rinsing and dying.
Unless present prior to shipment from the galvanizer, the development of wet storage stain is not the responsibility of the galvanizer. The customer must exercise proper caution during transportation and storage to protect against wet storage staining.
Figure 21.
